Set Up Domain Name which uses a Dynamic IP
The Problem
I have finally broken down and purchased a couple domain names (to cover <mydomain>.com and <mydomain>.ca) - they were quite simply too cheap not to buy. The problem is I have residential high-speed service which uses dynamic IP assignment to my modem and even though I am only using the dns/ip for development and testing of work at this point, I need the name to resolve to a web server on a Hyper-V virtual machine and to update the ip in my nameserver records whenever it changes. Static record pointing to a dynamic IP which resolves internally to a dynamic IIS site on a dynamic Hyper-v server. Wee!
The Approach
The first step is to find a free or cheap way to automate my A records. A bit of Googling turned up a couple of options. I found DynDNS to be pretty expensive for my needs (it cost more than the price of the domains at the time of writing ...) so opted for
EntryDNS. The one time donation / fee is very appealing and the few reviews I checked out gave this site high praise. The whole point of this service is to manage A records and to allow dynamic update of IPs using basic url requests. So I signed up.
Next I went to the registar of my domains and dug through the documentation until I found how to assign third party name servers to my record and changed them to ns1.entrydns.net and ns2.entrydns.net ... then waited for a full day for this change to propogate (I guess there was a reason for the sale ...)
In the mean time I set up my router, modem and server (hyper-v host running Win 10 pro) to port forward requests on port 80 through 443:
Modem - dynamic external IP, internal dynamic (192.168.x.x) IP assignment. Setup port forwarding of all incoming port 80 to 443 requests to the IP of my internal sub-net Router's IP (192.168.0.1)
Router, dynamic external IP (192.168.0.1 preferred), internal static IP ranges 10.0.0.X/24 I set up port forwarding (192.168.0.1/24:80) to my Hyper-v server (10.0.0.4/24:80).
$serverExternalIP = "10.0.0.4"
#Internal IP of the host Windows 10 server
$serverInternalIP = "10.0.99.1"
#the 10.0.99.x part must be the same as the $IPRange below and the .x part must be 1
$IPRange = "10.0.99.0/24"
# NAT sub-domain to be used with this connection
$DestinationHyperVServer = "10.0.99.225"
# this is the IP of the Hyper-v Server with the IIS service running (and SharePoint in my case)
# Run Get-NetNat first to see if you already have a defined net service running
New-VMSwitch -Name "NAT" -SwitchType NAT -NATSubnetAddress $IPRange
New-NetIPAddress –IPAddress $serverInternalIP -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (NATSwitch)"
# change the IP address of the host, Windows 10 Server to match the range with the first IP
New-NetNat –Name NAT –InternalIPInterfaceAddressPrefix $IPRange
Add-NetNatStaticMapping -NatName “NAT” -Protocol TCP -ExternalIPAddress 0.0.0.0 -InternalIPAddress $DestinationHyperVServer -InternalPort 80 -ExternalPort 80
Add-NetNatExternalAddress -NatName "NAT" -IPAddress $serverExternalIP -PortStart 80 -PortEnd 443
Get-NetNatExternalAddress
Get-NetNatStaticMapping
Get-NetNat

Next I set up a basic Hyper-V farm consisting of 3 servers (using the 2012 server r2 developer trial) using the Virtual Switch NAT created by the PowerShell as follows:
AD (dns and Active Directory Services for my two purchased domains - all settings in PowerShell to enable quick building) IP set internally to 10.0.99.2, Subnet 255.255.255.0 and Gateway set to the Host system internal NAT IP (10.0.99.1 in this case)
CLS set to use 10.0.99.3 in DNS.
IP4 settings of DNS servers set to Google (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) with the DNS suffix of my domain appended in advanced dns settings (not sure if this is necessary but it doesn't hurt so ...)
Then I joined the server to the newly created Domain.
Left the window open to allow record adding when other servers join the domain.
IIS (IIS/SharePoint development server)
Pretty much the same IP settings except the IP address was set to 10.0.99.225 and the Alternate DNS server ip set to 10.0.99.2 (so the internal DNS service resolves internal names). IIS initially set up to just HTTP and no bindings.
SQL (Sql Server 2012) IP in the unused 10.0.99.x range, same settings as the IIS server other than that.
Testing is pretty simple - browse to localhost and 10.0.99.225 from the IIS machine - both should produce a site. Browse to 10.0.99.225 on SQL and AD - should see the same site. From the hyper-v host, browse to 10.0.99.225, 10.0.0.4 (whatever it's internal ip address is) and whatever your external IP is (from the modem) - all three should open the same site.
Once the nameservers have refreshed and your whois record shows them as being used, test the domain name on both the server and host level.
For SharePoint I set up AAM for each of the subsites to go to different applications at the same IP and this worked well but will not go into detail here.
Now came the fun part. I created the following PowerShell script to handle updating the dynamic IP recorded on the EntryDNS service. This uses the Doman record Tokens in a string array - I'll likely change this to read an input file of either CSV or XML delimited values.
The global logic is as follows:
Get the current public internet IP (from checkip.dyndns.com), compare to the last recorded IP address registered and if different update the EntryDNS entry and the IP record. Then set up a timed job to run the script on a regular interval.
The code:
#DNS Codes for each domain entered in EntryDNS
$Codes = ("put the codes here")
#this is a simple text file with a single IP address inside it Change to any location you like for a temp file (C:\temp or something)
$IpFile = "C:\IP.txt"
# set to true to debug the settings. Logging is very verbose so not a good idea to leave on.
$logging = $false
$logpath = "C:\testlogs\"
function UpdateEntryDNS ($Code, $currentIP) {
try {
$req = "https://entrydns.net/records/modify/$Code"+"?ip="+"$currentIP"
# Builds the url to update the IP address
$r = Invoke-WebRequest $req
if ($logging -eq $true) {
$dt = Get-Date -Format g | foreach {$_ -replace ":", "."}
$fn = "$logpath"+$dt+$Code+".txt"
# if the path doesn't exist, create the directory
if ((Test-Path($logpath)) -eq $false) {mkdir $logpath}
# output file and populate with details
# interval of checking should be at least 1 min apart or files get overwritten
$Logoutput = "$dt "+ $r.StatusCode +" " +$r.Content+" "+$req | Out-File $fn -Force
}
Write-Host "Updated"
}
catch {
}
}
function Get-ExternalIP {
# the following parses the returned page
# changing the source will mean parsing the returned content appropriately.
$Ip =(Invoke-WebRequest "checkip.dyndns.com").Content
$Ip2 = $Ip.ToString()
$ip3 = $Ip2.Split(" ")
$ip4 = $ip3[5]
$ip5 = $ip4.replace("</body>","")
$curIP1 = $ip5.replace("</html>","")
$curIP = ($curIP1.replace("`n","")).Trim()
return $curIP
}
$currentIP = Get-ExternalIP
# if the file exists, read it - otherwise run once with null IP and create file with current IP
if (Test-Path($IpFile)) {
$content = ([IO.File]::ReadAllText($IpFile)).Trim()
}
else {
$content = "0.0.0.0"
}
# New IP
if ([IPAddress]$content -ne [IPAddress]$currentIP) {
Write-Host "Updating ... "
Write-Host "Old IP: " $content
Write-Host "Current IP: " $currentIP
# (Over)Write new Ip Addres to file
$currentIP | Out-File $IpFile -Force
# update dns for all in list
ForEach ($Code in $Codes) {UpdateEntryDNS $Code $currentIP}
}
# No New IP
else {
Write-Host "Equal"
}
Running the above will create the file C:\IP.txt which contains the most current IP address, a folder located at C:\testlogs\ if logging is changed to $true with a timestamp+code named file for each update attempted - inside each is the return code and content message (200 and OK are the desired results here) as well as the combined URL used for debugging purposes.
Now that this has been created and tested, save it to a good location for custom scripts on the Windows 10 Host system (C:\powershellscripts for instance) and set up a timed event to run the script.
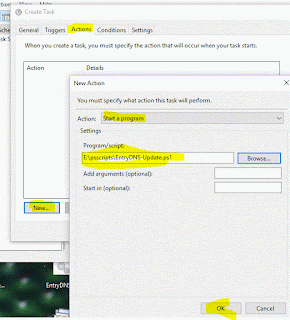
Open "Administrative Tools' and 'Task Scheduler' and click 'Create Task'
Give it a meaningful name
Create a trigger and set up the timing as suits your environment (no more than once every 5 minutes is recommended and remember to enable 'Stop Task if it runs for ...' to kill any hanging processes eventually. Click OK.
Next Add the Action. Action Tab -> New -> select Start a program -> Find the script above, click OK.
Click ok and ok and close all those nasty windows!
Voila! Minimal downtime when the IP changes.
Note that one still needs to add DNS entries for subsites in SharePoint (in AAM) and in DNS (EntryDNS which adds more update codes to the list) and in IIS (to some degree). Ideally a Site creation script used in this environment will do all of that in one step.
The Result
A relatively simple PowerShell script which can be reused on a timed basis to keep my IP up to date with my server.
Going Forward
Potentially use a csv / text file to manage multiple domains, sub-sites and keys to update the A record of each (in the absence of figuring a way to use a wildcard).
If other free-ish services are available, add routines for each so a simple toggle can be selected in the script for parsing of both the IP resolution and the entryDNS site.
If this helped, let me know! If it is broken, Let me know!